|
By Katy Cameron, Carleton Graduate Student Author’s Note: I would like to acknowledge that I am but one First Nations voice of many and recognize the diverse and unique experiences of Indigenous People across Turtle Island.  Source: Kamloops This Week, 2021 Source: Kamloops This Week, 2021 We are approaching two years since the initial discovery of the remains of 215 Indigenous children buried at the former Kamloops Indian Residential School in British Columbia, Canada. It came as shocking news for some and was a tragic confirmation for many Indigenous Peoples of what had long been suspected. For me, feelings of sadness and despair surfaced for my family and friends who experienced the Residential School system firsthand or were impacted by its legacy effects. Several of these schools were places that separated families, stripped children of their cultural traditions and knowledge, performed experimentations, and turned a blind eye to sexual and violent abuse. Only in the past decade or so has colonialization been acknowledged as a unique social determinant of health for Indigenous Peoples and efforts been made to understand its role in contributing to the disproportionate levels of chronic disease experienced by this population (Reading & Wien, 2009). But how exactly does colonization and its legacy impact the development of chronic disease, and why is this still a problem in 2023?  Source: Crown-Indigenous Relations and Northern Affairs Canada, 2022 Source: Crown-Indigenous Relations and Northern Affairs Canada, 2022 Diabetes, heart disease, arthritis, and cancer are all examples of chronic diseases in which environmental and/or individual factors promote the development of health conditions that are present for extended periods of time (Earle, 2011). It is commonly known that practicing healthy habits such as eating nutritious foods, getting enough sleep, and regularly exercising contributes to healthier outcomes and reduces the risk of developing chronic diseases and illnesses. Sounds easy enough, right? For many Indigenous people, however, the reality is that there are numerous social barriers to engaging in healthy behaviours. In the first-ever Indigenous Services Canada Annual Report to Parliament in 2020, Indigenous Peoples, especially First Nations living on-reserve, reported lower incomes, less education, reduced employment rates, worse housing conditions, and decreased life expectancy compared to non-Indigenous counterparts. They also reported greater likelihood of being in foster care and higher infant mortality rates, as well as higher rates of violence, victimization, and incarceration. This exemplifies the magnitude of the inequities experienced by this population, and it is understandable why Indigenous Peoples are at greater risk for developing disproportionate rates of disease, illness, and even deaths. Conversely, a study conducted by Anand et al. (2019) found that First Nations communities with higher incomes, better education, increased access to healthcare services, and robust social support mechanisms displayed fewer risk factors for cardiovascular disease compared to communities with overall lower socioeconomic status. Moreover, other research indicates that socioeconomic and lifestyle factors contribute to the high proportion of First Nations who suffer from diabetes (Halseth, 2019). These findings support the position that the social determinants of health play a significant role in contributing to the subsequent development of chronic disease amongst First Nations and other Indigenous groups. 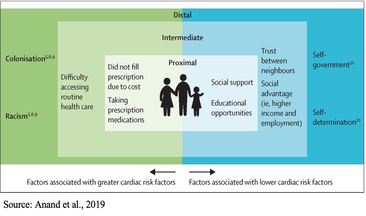 So, how does colonization and its legacy effects tie into chronic health disparities? According to one article, there are proximal, intermediate, and distal social determinants at play. Proximal determinants are those that directly impact healthy behaviours (e.g., physical environment), intermediate determinants are institutional or system-specific (e.g., education level and health care accessibility), and distal determinants are the bigger-picture issues from which many of these factors stem, such as colonialism and racism. Colonialism has been defined as the exploitation, control, and settlement of one country by another (Blakemore, 2019). In Canada, this involved removing autonomy from Indigenous Peoples and using assimilation strategies such as Residential Schools, separating children and families through the Sixties Scoop, and continues today by disproportionately placing Indigenous children in the Child Welfare System (Hobson, 2022). For many Indigenous families, the proximal effects of these initiatives resulted in broken-family dynamics and unstable living situations, depression and overall poor mental health, a loss of sense of self, and substance use. Furthermore, intermediate effects such as a lack of access to, or affordability of, adequate treatment services for these outcomes have ultimately led to intergenerational traumas, and high rates of suicide (Bombay et al., 2014), and we are now seeing higher prevalence rates than ever of chronic diseases like diabetes amongst First Nations youth (Halseth, 2019). If we know that colonialism has shaped both the social determinants and direct health outcomes of Indigenous Peoples (i.e., increased chronic diseases), why do these issues continue to persist? 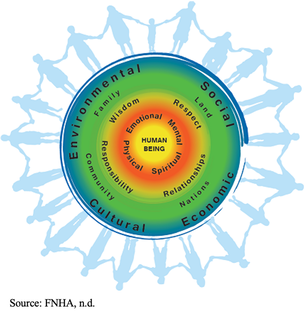 In 2015, the Canadian Government accepted the final report released by the Truth and Reconciliation Commission of Canada, which outlined 94 Calls to Action targeted at improving Indigenous health, education, and other domains. Although efforts have been made towards addressing these Calls, colonialism persists through current Westernized structural and governance frameworks, policies, and practices that continue to perpetuate the disadvantages and inequalities experienced by Indigenous Peoples in Canada (Blanchet Garneau et al., 2021; Czyzewski, 2011). Prime examples of this can be seen with policing issues, the overrepresentation of Indigenous People in the Canadian criminal justice system (Clarke, 2019), and insufficient culturally sensitive health educational programming, which can result in discrimination and harmful stereotyping (Blanchet Garneau et al., 2021). Increased collaboration and open communication between different levels of government and Indigenous leaders are needed to act on the chronic health disparities we know disproportionately affect Indigenous Peoples. Targeting the social determinants that impact this population, by increasing employment and educational opportunities and guaranteeing equitable access to basic necessities such as adequate healthcare and clean drinking water, is needed in order to ensure better health outcomes for future generations. As we are reminded of the horrific truths about the history of the Residential School system and the effects of colonialization through continued media reports of more unmarked graves, remember that the effects of colonialism are not a thing of the past. In fact, we still see the legacy effects on Indigenous health today, if we are willing to look. References:
This blog was originally written as part of the HLTH5402 course.
1 Comment
4/27/2023 05:43:25 am
Thank you for this article. It was very useful. I appreciate the research and effort you put into this post. It shows.
Reply
Your comment will be posted after it is approved.
Leave a Reply. |
Archives
March 2023
Categories
All
|
 RSS Feed
RSS Feed